Develop: Error Handling with RAISERROR and UserNotice
Estimated reading time: 3 minutesOverview
This page will cover error handling in Interject development using T-SQL’s RAISERROR and Interject’s UserrNotice flag.
Understanding Error Handling
There are two types of errors that Interject can display: unhandled and handled. Unhandled errors are system generated, whereas handled errors are anticipated and written by developers. For example, on a pull or save, an error may occur on the server which the report is trying to access. This error could be handled by the developer if the developer anticipates it, or it could be left as an unhandled error.
Error Handling With RAISERROR
Interject leverages the T-SQL statement RAISERROR in its Data Portals to process errors.
RAISERROR is designed to generate error messages and initiate error processing in the session (Source: Microsoft RAISERROR Documentation). It is used as follows:
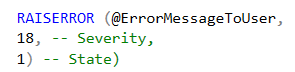
@ErrorMessageToUser - a string containing a description of the error, with or without a prefix of ‘UserNotice:’.
severity - generally a number from 0-18 ranking the severity of the error, typically 18 if you want to stop the execution of a stored procedure.
state - number, 0-255, used to locate where errors occur in your code.
- See Microsoft RAISERROR Documentation from more detailed information on using RAISERROR and its parameters.
Error Handling With UserNotice
UserNotice: is an Interject-defined identifying string that we append to the beginning of the @ErrorMessageToUser argument at the time of passing to RAISERROR to indicate that we would like a popup to appear to the user in Excel when the error occurs. It is used as follows:

When UserNotice: is added to your @ErrorMessageToUser before being passed to RAISERROR, it enables the option of having a popup window appear, alerting the user of the error in Excel.
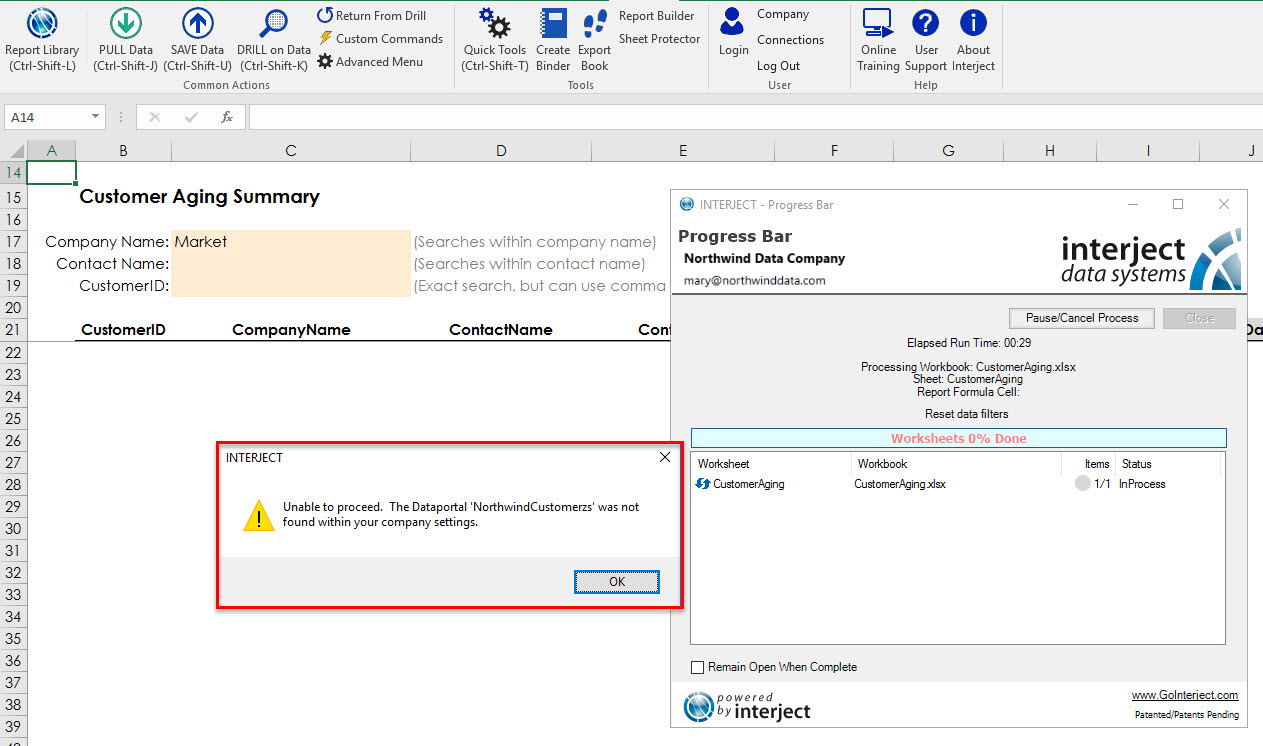
Errors can quickly be handled (as opposed to leaving them unhandled) by developers simply by using the UserNotice string.
Unhandled Error Behavior
If you opt not to use UserNotice, your error will still be reported by the Interject Add-in, but no popup window will appear for the user: