Defining Interject for Developers
Estimated reading time: 3 minutesOverview
Before you get into the details and hands-on examples for developers, it is important to explain how the Interject platform works. Interject directly links a database stored procedure or website API to the Excel interface, in a similar way that middle-tier logic connects to a website application.
Developers often assume that Interject is useful only in building simple reports, not extending to workflow creation or collecting user inputs. However, Interject is truly an application platform that can extend reports into two-way interfaces, which have the impact and scalability of a website application.
Two Basic Concepts Go a Long Way
The Interject process starts with two basic concepts.
- Interject connects Excel to a middle-tier service that communicates with external or internal data sources. It supports retrieving and saving data.
- Interject navigates and drills between spreadsheet tabs within the Excel application like a multi-page website.
Data Workflow
The simplified diagram below illustrates the flow of data through the Interject platform. Users log in to Interject, which then returns settings, including the data connection configuration, that can be used in spreadsheet applications. The Interject Add-In in Excel uses these settings to build reports and apps that leverage the connection configuration to directly link a user session to a middle-tier service, such as a stored procedure in a database or a data web service (a data API).
When Interject makes the connection between the user session and the middle-tier service, their authentication context is passed through so you can handle security and row-level views as needed.
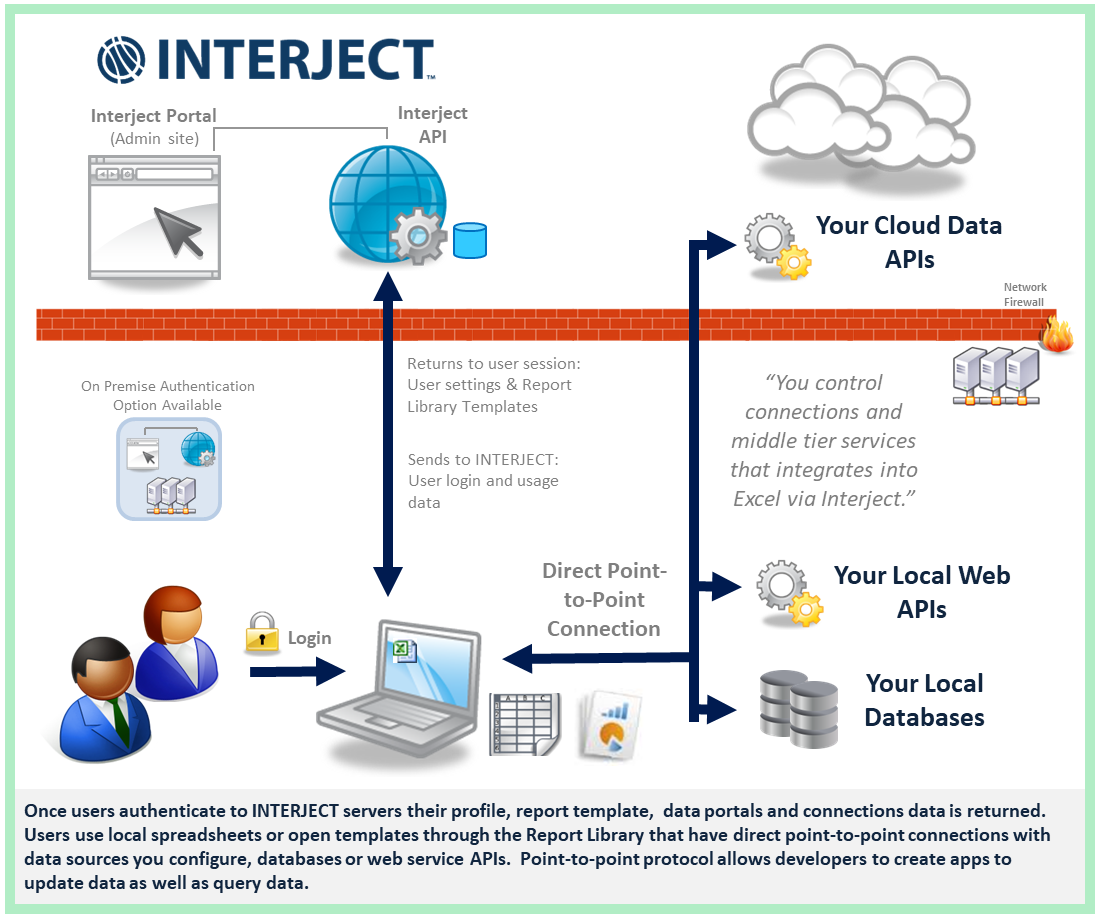
The illustration above shows the cloud model of the Interject platform, but there are hybrid models that allow for full on-premise dependency.
Managing the distribution of spreadsheet reports or apps is just as important as building the spreadsheet app itself. Interject provides the Report Library to publish reports so they are quickly accessible while still protecting and tracking versions of the source templates. The process also begins to teach users that they can access their data without repeatedly saving files locally, just like they learned with website applications. Publishing reports and apps can be done through other file-sharing tools or corporate intranets as well.